所以啊,为什么刚读完题就感到手疼了呢?QwQ
题目简述
题目比较复杂——没有玩过音游的小伙伴们建议从上面的链接前往原题
下落式音游。给出判定的时间规则,每个 Key 的位置范围和到达判定线的时间,每次 Click 的位置和时间,统计 miss,good,perfect 和 maxcombo。
思路:
数据结构的使用
Key 的位置是一个范围,在判定线上投影为一段区间,Click 的位置是一个点,在判定线上投影为一个点——处理每一次的 Click,对 Key 进行判定,其实就是在一条线段上以一个单点为入口对区间进行判定——于是我们可以用线段数来维护 Click 和 Key 的信息。
一般来讲线段树可以看作是一种二维数据结构,两个维度分别是「位置」和「层级」:在访问某一个位置的时候我们从「位置」出发,在「层级」上推进,最终找到我们要访问的数据在线段树中的具体位置。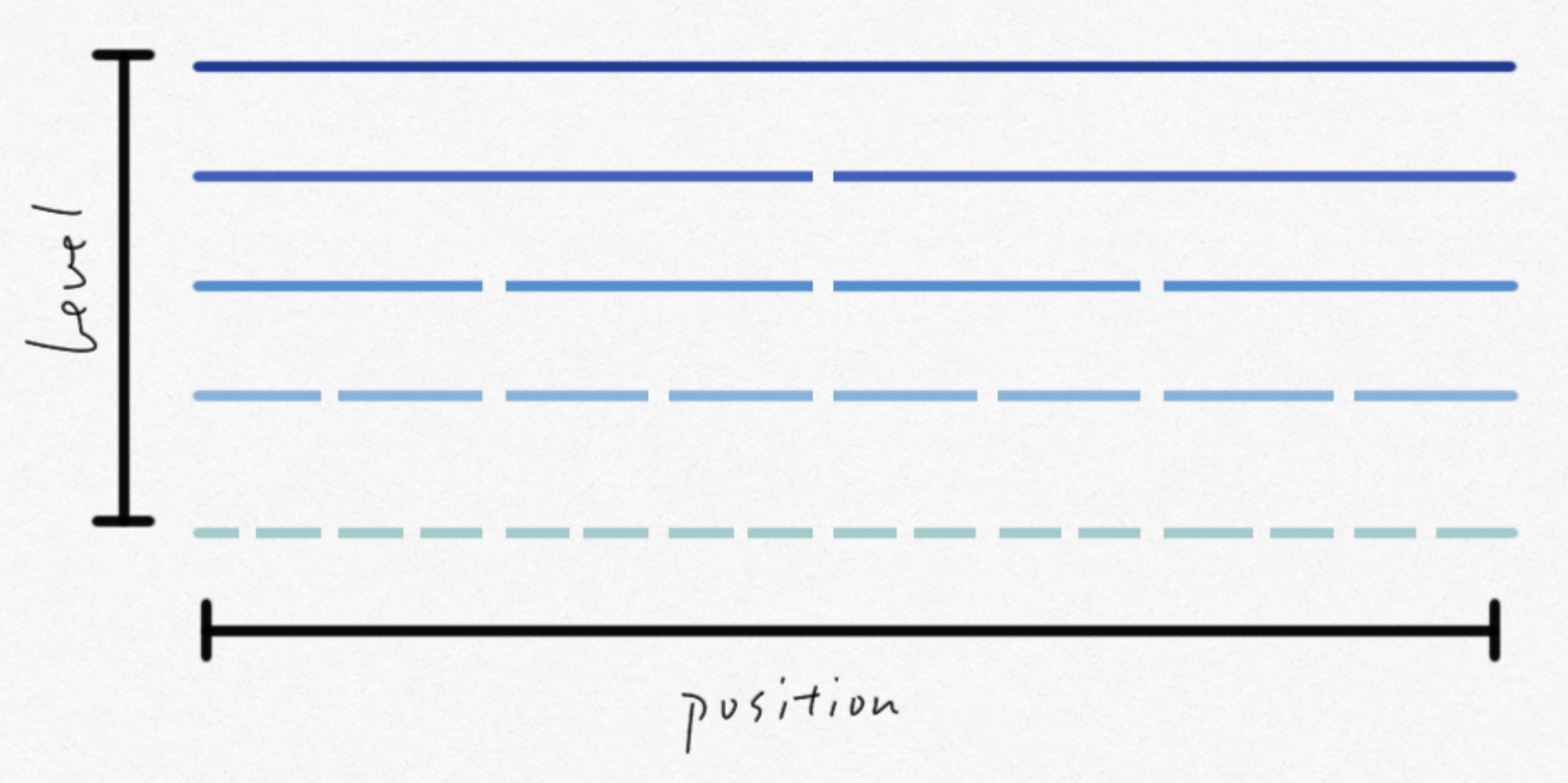
但是在本题中,判定线上的同一位置可能会出现多个 Key,这些 Key 在「位置」和「层级」维度记录的数据都是相同的,但是它们出现的时间是不同的——换句话说,二维的线段树已经满足不了我们统计数据的需要,我们应该在二位线段树的基础上增加一个「时间」维度。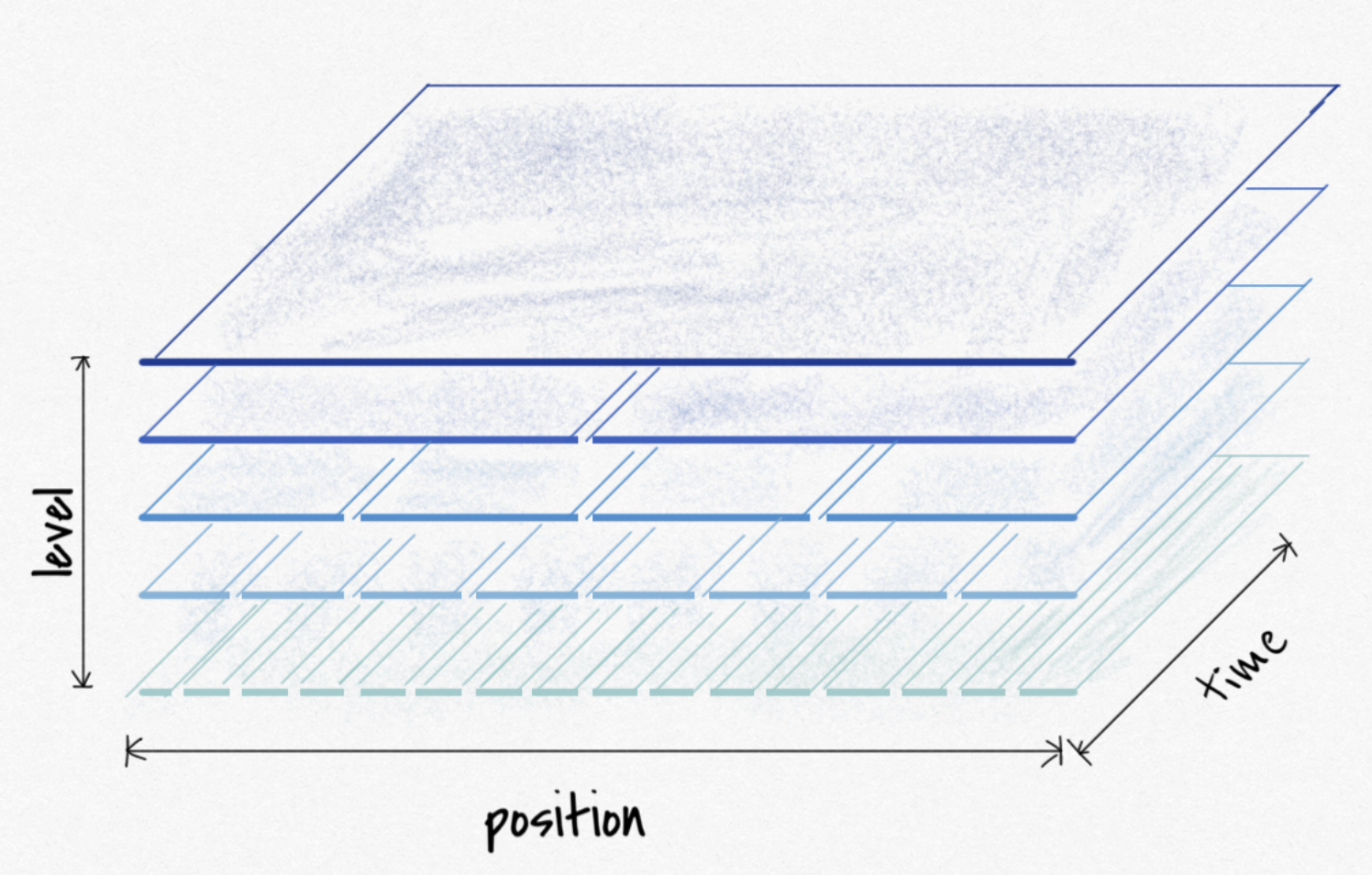
从上面的线段树分析中我们可以看出:线段树的几个维度并不是平行关系,其从主到次的顺序分别是:「位置」「层级」「时间」
数据处理
位置和时间都是最多五位的小数,为了计算方便,我们将所有数据乘 10^5^,用整数表示位置和时间,为了防止产生精度误差可以用「四舍五入」的方式加上 0.5。将数据离散化并且将 Key 和 Click 按照时间排序方便线段树时间维度的构造以及答案的统计。
将 Key 放入线段树
方法与二维线段树几乎相同。
在原来的线段树中当查找到线段树最底层时,也就意味着第二个维度也走完了,我们只需要将数据直接存入线段树的数组,而现在我们要在每一个位置都再扩展出一维:可以使用链表储存 Key 的编号,挂在线段树数组的每一个元素中。由于刚才已经将 Key 按照时间排过序,每一条链上的编号所指向的 Key 也是时间从前往后的——这样就成功构建出了我们所希望的三维线段树。
值得注意的一点是:原本的二维线段树对数组大小要求就已经很高了,再扩展一维会有更大的空间开销——再加上我们对位置进行了离散化处理,所以要把数组开大些。
对于 Click 和 Key 的判定
对于每一次 Click,我们需要求出它在那个具体的时间。事实上我们需要求出再有效打击时间范围内最前面的一个 Key,即对于时间为 $clickTime$,位置为 $pos$ 的 Click,我们要求 $judgeTime_{min}$ 满足 $a_i ≤ pos ≤ b_i$ 且 $clickTime-0.6s < judgeTime < clickTime + 1s$。然后对于我们求出的每一个 $judgeTime$ 判对可以判定的 Key 按照规则进行处理。
值得注意的一点是,判定过的 Key 我们要从线段树中删除——操作很简单但这是一个很重要的步骤。
答案的统计
最后按照判定时间对 Key 进行排序(以便计算maxCombo),扫一遍 Key 顺便就可以统计判定结果了
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<climits>
#define thisKey ky[nodeSerial[headNode[x]]]
using namespace std;
const int MaxN = 120000, Inf = INT_MAX;
int n, m, elemCount;
int missKey, goodTap, perfectClick, maxCombo, curCombo;
struct Key{int t, a, b, judgeTime, ifJudged;} ky[MaxN];
struct Click{int t, pos;} click[MaxN];
int nodeCount, headNode[MaxN << 4], lastNode[MaxN << 4], nextNode[MaxN << 10], nodeSerial[MaxN << 10];
bool cmpKey(Key x, Key y){return x.t < y.t;}
bool cmpClick(Click x, Click y){return x.t < y.t;}
bool cmpJudge(Key x, Key y){return x.judgeTime < y.judgeTime || (x.judgeTime == y.judgeTime && x.ifJudged < y.ifJudged);}
int posData[MaxN << 3];
inline int getPos(int x){return lower_bound(posData+1, posData+elemCount+1, x) - posData;}
inline void AddNode(int x, int ser){
//the x-th position on the segment tree with ser-th key
//it's worth noticed that for position x there may be more than one key with different serial
nodeCount++;
if(!headNode[x]) headNode[x] = lastNode[x] = nodeCount;
else nextNode[lastNode[x]] = nodeCount, lastNode[x] = nodeCount;
nodeSerial[nodeCount] = ser;
}
inline void Build(int l, int r, int reqL, int reqR, int x, int ser){
//in the traditional segment tree we can simply give a[i]'s value to the tree but here we need to used the AddNote function
if(l >= reqL && r <= reqR){AddNode(x, ser); return;}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(reqL <= mid) Build(l, mid, reqL, reqR, x*2, ser);
if(reqR > mid) Build(mid+1, r, reqL, reqR, x*2+1, ser);
}
//obviously the big number in the functions below comes from the 0.6 and 1 in game rule: after dispersing these numbers also get bigger
inline void Refresh(int x, int t){
//keys that have been clicked should be deleted
while(headNode[x]){
if(thisKey.t + 60000 <= t){
if(!thisKey.ifJudged){
thisKey.judgeTime = thisKey.t + 60000;
thisKey.ifJudged = 1;
}
headNode[x] = nextNode[headNode[x]];
}
else if(thisKey.ifJudged) headNode[x] = nextNode[headNode[x]];
else break;
}
}
inline int JudgeTimeCal(int x, int t){
if(thisKey.t - t >= 100000) return Inf;
else return thisKey.t;
}
inline int GetJudgeTime(int l, int r, int pos, int x, int t){
//delete judged keys before EVERY SINGLE TIME of JUDGE!
Refresh(x, t);
if(l == r) return JudgeTimeCal(x, t);
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(pos <= mid) return min(JudgeTimeCal(x, t), GetJudgeTime(l, mid, pos, x*2, t));
else return min(JudgeTimeCal(x, t), GetJudgeTime(mid+1, r, pos, x*2+1, t));
}
inline void Judge(int l, int r, int pos, int x, int t, int jt){
while(thisKey.t == t){
if(!thisKey.ifJudged){
thisKey.judgeTime = jt;
if(abs(thisKey.t - jt) < 20000) thisKey.ifJudged = 3;
else if(abs(thisKey.t - jt) < 60000) thisKey.ifJudged = 2;
else thisKey.ifJudged = 1;
}
headNode[x] = nextNode[headNode[x]];
}
if(l == r) return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(pos <= mid) Judge(l, mid, pos, x*2, t, jt);
else Judge(mid+1, r, pos, x*2+1, t, jt);
}
int main(){
//intput and have keys dispersed
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
double t, a, b;
scanf("%lf%lf%lf",&t,&a,&b);
ky[i].t = t*1e5+0.5, ky[i].a = a*1e5+0.5, ky[i].b = b*1e5+0.5;
posData[++elemCount] = ky[i].a, posData[++elemCount] = ky[i].b;
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
double t, p;
scanf("%lf%lf",&t,&p);
click[i].t = t*1e5+0.5, click[i].pos = p*1e5+0.5;
posData[++elemCount] = click[i].pos;
}
ky[0].t = Inf;
sort(ky+1, ky+1+n, cmpKey);
sort(click+1, click+1+m, cmpClick);
sort(posData+1, posData+1+elemCount);
elemCount = unique(posData+1, posData+elemCount+1) - posData - 1;
//add keys to the segment tree
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
Build(1, elemCount, getPos(ky[i].a), getPos(ky[i].b), 1, i);
//judge
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int clickPos = getPos(click[i].pos);
int t = GetJudgeTime(1, elemCount, clickPos, 1, click[i].t);
if(t != Inf) Judge(1, elemCount, clickPos, 1, t, click[i].t);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(!ky[i].ifJudged){
ky[i].ifJudged = 1;
ky[i].judgeTime = ky[i].t + 60000;
}
sort(ky+1, ky+1+n, cmpJudge);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(ky[i].ifJudged == 1) missKey++, maxCombo = max(maxCombo, curCombo), curCombo = 0;
else if(ky[i].ifJudged == 2) curCombo++, goodTap++;
else if(ky[i].ifJudged == 3) curCombo++, perfectClick++;
}
maxCombo = max(maxCombo, curCombo);
printf("%d %d %d %d", perfectClick, goodTap, missKey, maxCombo);
return 0;
}